Abstract
Background: CD19-targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T cell therapy has shown unprecedented results in patients with relapsed/refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (R/R ALL) where no other curative options are available. Despite a complete remission (CR) rate of 80%, more than half of the adult patients eventually relapse. Which patients are likely to benefit from consolidative treatment remains to be addressed. We conducted an academic, multi-center, phase I/II dose-escalation trial in ALL patients relapsed after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Patients received donor-derived, CD19-targeted CAR cytokine induced killer (CARCIK-CD19) cells engineered with the non-viral Sleeping Beauty transposon vector (Magnani et al. JCI, 2020).
Objective: The aims of this study were to evaluate the impact on clinical outcome of proliferation, differentiation, and expansion of infused CARCIK-CD19 cells.
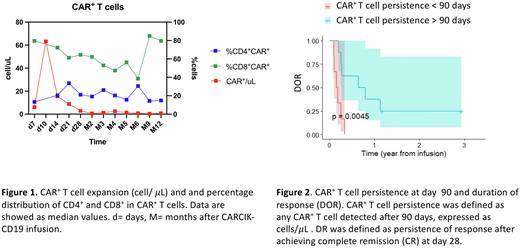
Methods: Data were prospectively collected from consecutive patients enrolled in the FT01CARCIK, Phase I/IIb study (NCT03389035), and a compassionate use study (FT02-CARCIKCD19). Patients underwent fludarabine and cyclophosphamide-based lymphodepletion, before CARCIK-CD19 infusion. For this study, only patients receiving cell doses previously shown to be well tolerated and effective (7.5x106/Kg [DL3] and 15 x106/Kg [DL4]) were included. CAR+ T cells were counted in the peripheral blood (PB) at predefined time points, using flow cytometry (FC). We assessed the distribution of T cell maturation subsets in infused CAR+ T cells, identified as: naïve (CD45RA+CD62L+), central memory (CM, CD45RA-CD62L+), effector memory (EM, CD45RA-CD62L-) T cells, and terminal differentiated T cells (TEMRA, CD45RA+CD62L-). Minimal residual disease (MRD) monitoring was performed using both FC and quantitative PCR (qPCR), in PB and bone marrow (BM). CR was defined as absence of leukemia in the BM at day 28. CARCIK-CD19 peak was defined as the maximum amount of CAR+ T cells/μL measured in PB. CAR+ T cell persistence was defined as any CAR+ T cell detected after 90 days, expressed as cells/μL. Duration of response (DOR) was defined as persistence of response after achieving CR at day 28.
Results: This analysis included 20 patients treated with CARCIK-CD19 cells from October 2018 to October 2021, 15 of whom were enrolled in the Phase I/IIb study and 5 patients in the subsequent compassionate use study. CR rate at day 28 was 76.2% (95% CI= 52.8-91.8%), of which 81.3% were MRD negative. The median OS was 12 months. The OS at 6 months was 71.4%. Circulating CAR+ T cells peaked at day 10, with a median of 48.5/μL (range, 0.6-718), whereas the median value at day 28 was 2.6/μL (range, 0-33.2). CAR+ T cells were still detectable at month 12 with a median of 0.8/μL (range 0-2.2) (Figure 1). As shown in Figure 1, the majority of CAR+ T cells were CD8+ T cells. At day 7 the majority of CAR+ T cells were CM with a median of 31.7% (range, 0.7-90) and EM T cells with a median of 25% (range 7-96.5), but we still observed a high percentage of Naïve CAR+ T cells, with a median of 9.9% (range, 0-47.9) and TEMRA, median 4.5% (range 0-32.9). Instead, on day 28 the majority of CAR+ T cells were EM, with a median of 33.7% (range, 0-96.8), followed by CM T cells, median 22.1% (range, 0-77.8), Naïve, median 10.2% (range, 0-66.66), and TEMRA, median 10% (range, 0-49.9). A negative MRD status in the BM at day 28 assessed by FC positively correlated with OS (p=0.004). In addition, the persistence of CAR+ T cells after day 90 correlated with DOR (p= 0.0045, Figure 2).
Conclusions: In this study we showed that CARCIK-CD19 cells efficiently expanded in vivo, reaching the peak at day 10, and persisting in some cases until 12 months after infusion. The majority of CAR+ T cells were CD8+ with a memory phenotype confirming the capability of these cells to persist long-term. CAR+ T cells persistence was associated with a longer duration of response and reduced risk of leukemia relapse. The achievement of a negative MRD status at day 28 was crucial for patient's survival, suggesting the need of early additional treatment in patients failing this end point.
Disclosures
Rambaldi:Equillium: Other: support for attending meeting. Magnani:Nanocell: Consultancy. Lussana:Janssen Oncology: Honoraria; Incyte: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; Astellas Pharma: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy. Gritti:Genmab: Other: Advisory Board (2022); Beigene: Other: Training activity (2022); Ideogen: Other: Advisory Board (2022), Training activity (2022); Sandoz: Other: Support for attending meetings (2021); Clinigen: Other: Training activity (2021); IQVIA: Other: Advisory Board (2020); Kite-Gilead: Other: Advisory Board (2020); Italfarmaco: Other: Advisory Board (2021); Takeda: Other: Advisory Board (2020, 2021, 2022), Training activity (2020, 2022), Individual scientific consultancy (2021-ongoing); Roche: Other: Advisory Board (2021) Training activity (2020), Support for attending meetings (2021); Incyte: Other: Training activity (2022). Rambaldi:Incyte: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Jazz: Honoraria; Omeros: Honoraria; Celgene-BMS: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria; Roche: Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria; ABBVIE: Honoraria; Kite-Gilead: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria. Biondi:Amgen: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Bluebird: Other: Advisory Board (2020); Incyte: Other: consultancy and other advisory board.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.